Over the past decade, GLP-1 medication has transformed the way doctors approach chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and obesity. These drugs, known as GLP-1 receptor agonists, not only help regulate blood sugar but also promote significant weight loss and reduce cardiovascular risks. From being a niche treatment option to becoming one of the most in-demand therapies worldwide, GLP-1 medication is reshaping modern healthcare.
This detailed guide will cover everything you need to know about GLP-1 medications, including how they work, their medical uses, benefits, side effects, comparisons between different types, and what the future may hold for this class of drugs.
What Is GLP-1 Medication?
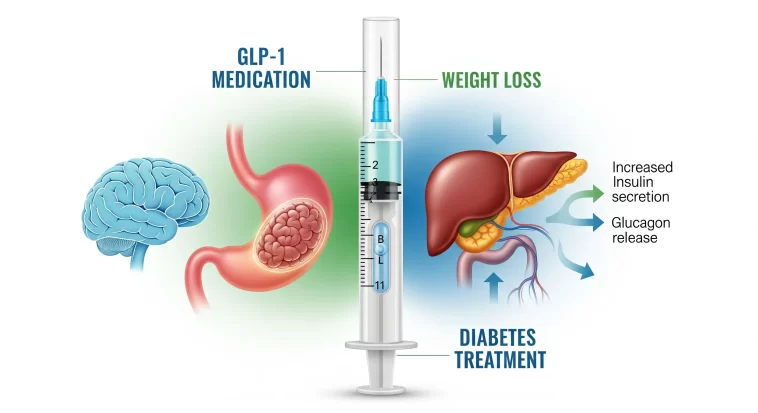
GLP-1 stands for glucagon-like peptide-1, a hormone naturally produced in the gut after eating. Its primary role is to:
- Stimulate insulin release when blood sugar is high
- Suppress glucagon secretion (which normally raises blood sugar)
- Slow gastric emptying, helping you feel full for longer
- Reduce appetite and food cravings
When scientists discovered how powerful GLP-1 is in controlling both blood sugar and hunger, they developed synthetic drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs mimic the natural hormone, offering patients a long-lasting way to regulate appetite and improve metabolism.
Different Types of GLP-1 Medications
Several GLP-1 receptor agonists are now available, each with slightly different effects, dosing schedules, and brand names:
- Semaglutide – Found in Ozempic (weekly injection for diabetes), Wegovy (weekly injection for obesity), and Rybelsus (oral tablet).
- Liraglutide – Marketed as Victoza (for diabetes) and Saxenda (for obesity), taken as a daily injection.
- Dulaglutide – Known as Trulicity, a weekly injection used primarily for type 2 diabetes.
- Exenatide – Available as Byetta (twice daily) and Bydureon (once weekly).
- Tirzepatide – Marketed as Mounjaro, it is a dual GIP/GLP-1 agonist, which means it targets two hormones instead of one, showing even greater weight loss results.
Each of these medications works similarly but may differ in effectiveness, convenience, and tolerance.
How GLP-1 Medication Works
The mechanism of GLP-1 medication is both simple and powerful. By mimicking the body’s natural hormone, these drugs create multiple health benefits:
- Regulation of blood sugar – Insulin release is triggered only when blood sugar is high, lowering the risk of hypoglycemia compared to traditional diabetes drugs.
- Appetite control – GLP-1 medications act on the brain’s appetite centers, reducing cravings and helping patients feel fuller faster.
- Delayed gastric emptying – Food stays in the stomach longer, leading to reduced calorie intake.
- Weight loss support – By reducing overeating and cravings, patients naturally eat less and lose weight steadily.
- Cardiovascular protection – Many GLP-1 medications have been proven to lower the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
GLP-1 Medication for Type 2 Diabetes
When GLP-1 medications were first approved, their primary use was for type 2 diabetes treatment. For patients who struggled to control blood sugar with diet, exercise, or oral medications like metformin, GLP-1 receptor agonists offered a new solution.
Benefits for diabetes patients include:
- Lower HbA1c levels (average blood glucose over 3 months)
- Reduced risk of hypoglycemia compared to insulin
- Weight loss support (which further improves diabetes control)
- Cardiovascular protection in high-risk patients
Because of these combined effects, GLP-1 medications are now recommended by international diabetes guidelines as one of the top treatment choices.
GLP-1 Medication for Weight Loss
Perhaps the most widely discussed benefit of GLP-1 medication today is its use in weight loss.
Clinical trials have shown that:
- Semaglutide (Wegovy) can help patients lose an average of 15% of body weight in just over a year.
- Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) has shown even more dramatic results, with patients losing up to 20–22% of body weight in clinical studies.
- Liraglutide (Saxenda) also produces significant weight loss, though less than semaglutide.
These results rival or even surpass many bariatric surgeries, making GLP-1 medications a game-changer in obesity treatment.
Weight loss with GLP-1 drugs is not just about aesthetics—it reduces the risk of:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Sleep apnea
- Type 2 diabetes
- Fatty liver disease
- Joint problems
Additional Benefits of GLP-1 Medications
While diabetes and obesity are the main targets, research shows that GLP-1 receptor agonists may have broader benefits:
- Cardiovascular health – Reduced risk of major heart events.
- Liver protection – Promising results in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Kidney benefits – May reduce the risk of kidney complications in diabetes.
- Mental health impact – Early studies suggest GLP-1 medications may reduce food addiction, binge eating, and even depression related to obesity.
- Neurodegenerative diseases – Ongoing trials are investigating GLP-1 in conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Side Effects of GLP-1 Medications
Like any medication, GLP-1 drugs come with side effects. The most common include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Stomach pain
Most of these occur when starting treatment and may improve as the body adjusts.
Rare but serious risks include:
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- Gallbladder disease
- Kidney injury in vulnerable patients
- Possible thyroid tumors (seen in animal studies, not yet proven in humans)
Because of these risks, GLP-1 medications must be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional.
Comparing Different GLP-1 Medications
| Medication | Brand Names | Dosing | Primary Use | Average Weight Loss | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semaglutide | Ozempic, Wegovy | Weekly (inj.) / Daily (oral) | Diabetes + Obesity | 15%+ | Most effective, widely used |
| Liraglutide | Victoza, Saxenda | Daily injection | Diabetes + Obesity | 5–10% | Older but effective |
| Dulaglutide | Trulicity | Weekly injection | Diabetes | Moderate | Easier dosing |
| Exenatide | Byetta, Bydureon | Twice daily or weekly | Diabetes | Moderate | First GLP-1 approved |
| Tirzepatide | Mounjaro | Weekly injection | Diabetes + Obesity | 20–22% | Dual-action (GIP + GLP-1) |
Who Should Consider GLP-1 Medication?
GLP-1 medications may be recommended for:
- People with type 2 diabetes who cannot achieve blood sugar control with other medications.
- Individuals with a BMI over 30 (obesity).
- People with a BMI over 27 with weight-related health problems (hypertension, diabetes, sleep apnea, etc.).
- Patients at high cardiovascular risk.
However, GLP-1 medications are not suitable for everyone. They are generally not recommended for:
- People with a personal or family history of thyroid cancer
- Those with pancreatitis history
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Patients with severe gastrointestinal disorders
Accessibility and Cost
One of the biggest challenges with GLP-1 medication is cost and accessibility. In the U.S., monthly prices for drugs like Ozempic or Wegovy can exceed $1,000 without insurance. While some insurance plans cover them for diabetes, coverage for weight loss treatment is more limited.
Globally, access varies widely. In some countries, GLP-1 medications are only available for diabetes treatment, not for obesity. This creates inequality in healthcare, as many people who could benefit cannot afford them.
The Future of GLP-1 Medication
The success of GLP-1 medication has launched a new era in pharmaceutical innovation. Researchers are exploring:
- Next-generation GLP-1 drugs that may be more effective and with fewer side effects.
- Oral formulations that eliminate the need for injections.
- Combination drugs, like tirzepatide, which target multiple hormones for greater results.
- New uses beyond diabetes and obesity, such as Alzheimer’s disease, PCOS, and even addiction.
Experts believe that GLP-1 medications could eventually become as common as statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs), prescribed to millions worldwide for chronic disease prevention.
Conclusion
GLP-1 medication is more than just a treatment—it’s a revolution in healthcare. From blood sugar control in diabetes to life-changing weight loss, these drugs are improving health outcomes for millions of people. While side effects and accessibility remain concerns, ongoing research continues to expand their potential.
In the coming years, GLP-1 medications may move beyond diabetes and obesity into a wider range of chronic conditions, making them one of the most important medical breakthroughs of the 21st century.
If you’re considering GLP-1 therapy, always consult with a healthcare professional to discuss risks, benefits, and whether it’s the right choice for you.