Research shows that nearly 600 plant species have disappeared in the last 250 years. The human factor is cited as the main reason for the extinction of plants.
Plants, like animals, become extinct over time for various reasons. Some have become extinct recently, others in the distant past. In fact, about 571 recorded plants have disappeared since the 1770s. Plants left the oceans about 400 million years ago and spread to terrestrial environments. To do so, they evolved in spectacular ways that you will find both familiar and strange. As modernization and climate change take hold, plants are becoming extinct at a much higher rate than at any other time in history. In this list, we have gathered answers to questions such as why plants become extinct and what are the endangered plants.
Why do plants become extinct?
There are many different reasons why plants go extinct:
Habitat loss: Plants face extinction when their natural habitat is destroyed or altered. Activities such as environmental pollution, deforestation, urban development and the expansion of agricultural areas cause habitat loss.
Natural disasters: Fires, floods and droughts are some of the factors that cause plants to become extinct.
Climate change: Climate changes cause the types of climate in which plants live to change. As a result of these changes, flowering times, seed yields and reproductive cycles of plants are negatively affected.
Human activities: Human activities such as the forest industry, mining, tourism, dam construction and agriculture can cause plant species to become extinct.
Diseases and plant pests: Various plant diseases can lead to plant extinction. In addition, the introduction of alien and pest plant species into native plant populations and disruption of the natural order can lead to the extinction of native plant species.
Hunting: Some plants important to humans are hunted for spices and traditional medicines. As a result of over-hunting, plant populations can be reduced and thus plants can become extinct.
What are endangered plants?
Over millions of years, many plant species have become extinct around the world. But in the last 250 years, more than 600 plant species have become extinct. Of course, the biggest reason for this is the human factor. Now we will tell you about some plant species that have become extinct.
Silphium

Silphium, an endangered plant, grew in the Roman city of Cyrene and its sap was valuable. The plant had small yellow flowers. Its fragrant sap was in such high demand that it was worth its weight in gold. The stem was cooked, the root was eaten raw and used to make meat dishes even more flavorful. Both perfume and valuable edible sap were made from the flower. Silphium was also a panacea for ailments, used as birth control and an aphrodisiac. In particular, it was used to treat a different form of malaria.
In ancient times, farmers tried to grow silphium but without success. The problem is believed to be that the seeds were not exposed to light to start the germination process and instead were left in the soil to rot.
Araucaria mirabilis
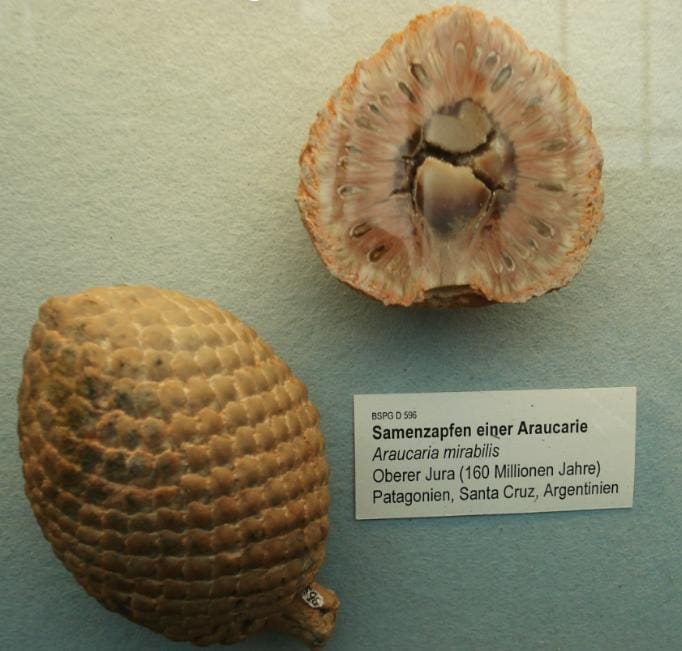

This tree grew over 125 meters tall. It was a coniferous tree that was destroyed in a volcanic eruption. It became extinct about 160 million years ago in its native Patagonia in Argentina. The eruption occurred when the pine cones on the trees were ripe, so locals in the area have been finding and preserving them for centuries.
Sigillaria
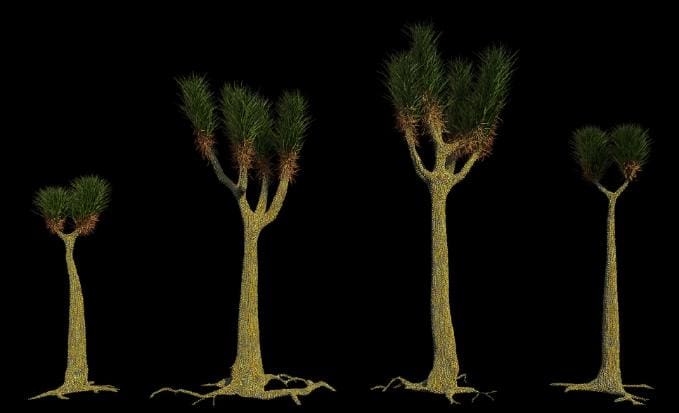

Sigillaria is one of the most common plant species from which fossil fuels are made. Sigillaria, which look like Joshua trees, flourished during the Carboniferous Period, 300 to 360 million years ago. It was found everywhere around the world. It liked peat bogs and released spores to reproduce. The spores came from cones hanging from its branches. Photosynthesis probably took place on its trunk. That’s why it’s thought to have a green color. It was also about 100 meters long.
Atriplex tularensis
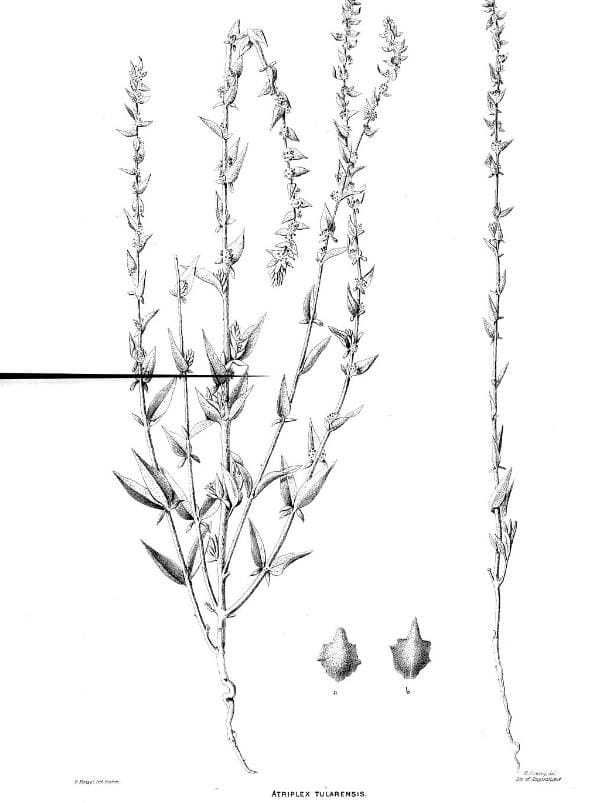
Atriplex tularensis was last seen in 1991. It was an annual plant that grew in the alkaline salt pans at the southern end of California’s Central Valley, only to be wiped out by the spread of weeds. As California’s Central Valley grew and became a world leader in agriculture, farmers and communities drained inland lakes and depleted deep underground water sources faster than mountain runoff could replenish them, depriving Atriplex tularensis of water.
Chilean sandalwood (santalum fernandezianum)
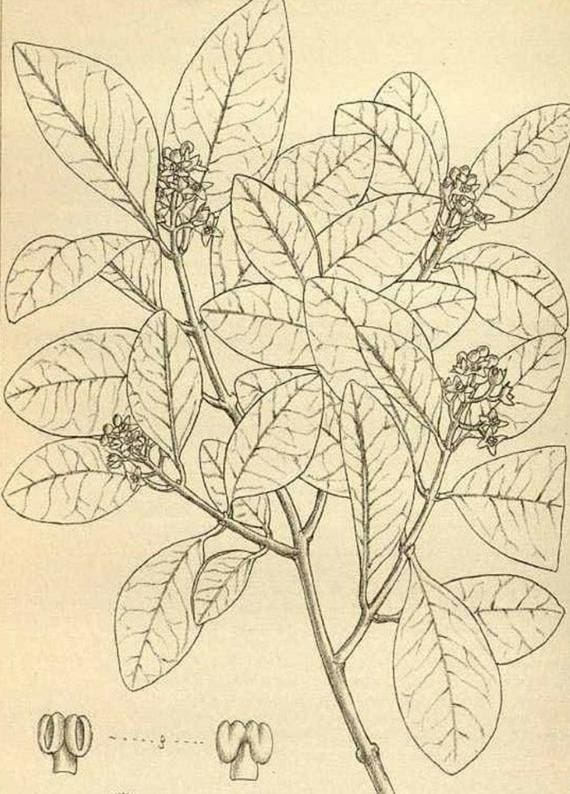
This tree became extinct because it was over-harvested for its fragrant wood. It was last seen in 1908 on Robinson Crusoe Island in the South Pacific. In 1750, the Spanish colonized the island and opened it to trade. This led to the extinction of the plant species.
Cooksonia

Cooksonia, one of the endangered plants, was a semi-aquatic plant and is likely to be the first plant to have a trunk. It lived on the coastline and was one of the first terrestrial plants on the planet. It appeared 400 million years ago. Although found worldwide, they were most common in Britain. At the end of their branches was a single capsule filled with spores, which they used to reproduce. They had a slightly leaf-like structure, but no true leaves. It was probably among the first vascular plants, which means it was the first plant to develop a system for transporting water throughout the plant.
Orbexilum stipulatum

Orbexilum stipulatum was a flowering plant native to Rock Island in the Ohio Falls and was last seen in 1881. A dam built in the area where this plant species grew flooded Rock Island, causing the plant to become extinct.
